AI AND BLOCKCHAIN - Why knowing one of them is guaranteed success in future?
"Software is eating the world" - Marc Andreessen
“Blockchain is like the new big data or AI - too many people are using it as a buzzword and not focused solving a real problem. We like to call them Blockchain tourists!” - Brad Garlinghouse
Over the past 2–3 centuries, the world has seen staggering change, starting with the industrial revolution that saw the transition to machines, the advent of chemical manufacturing, the invention of the steam engine, and the development of machine tools and mechanized factory systems termed as Industrial Revolution Phases 1,2 and 3. Soon after, we saw the invention of flight, changing how the world travelled. In our lifetime, we have seen the transformative effect the internet has had on humanity.
Now, we are seeing the rise of not one, but two technologies that are revolutionizing the world by using data:
Artificial Intelligence (AI) - Solve huge and complex problems through big data
Blockchain - Ensure trust and security of data
Companies and institutions are only just realizing the potential of these technologies and have begun deploying them, resulting in the complete transformation of industries. I have a strong belief in the revolutionary power of AI and blockchain. We are utilizing them in tandem to address the issue of inconsistent and incorrect metadata in the online video ecosystem.
Understanding AI
AI refers to machines capable of mimicking human intelligence thanks to complex algorithms that have been programmed into the code. This software is capable of thinking like humans, mimicking their actions, learning problem solving, rationalizing, and taking actions that have the best chance of achieving a specific outcome. AI can also learn from the data provided and getting smarter as it processes more data.
“Any sufficiently advanced technology is indistinguishable from magic.” - Arthur C Clarke
“Artificial intelligence, deep learning, machine learning – whatever you’re doing if you don’t understand it – learn it. Because otherwise you’re going to be a dinosaur within 3 years.” - Mark Cuban
Misuse of AI
Jason Allen from Colorado lit the fuse on a debate that's going to run and run he used AI software to create art, submitted it to the Colorado State Fair fine arts competition, and took first prize.
There are a few important facts to note. Allen did kind of acknowledge what he'd done, in crediting his submissions as being by "Jason Allen via Midjourney," and also spent considerable time working on the prompts to produce the eventual artworks: "many weeks" he says. He also worked further on the images Midjourney created in Photoshop, so they are manually finished. But of course, this is nuance next to the central issue: an AI artbot just beat out human artists and was clearly also plausible enough to fool human judges.
‘Midjourney’ is one of the many AI image generation tools (popular ones DALLE-2, Stable Diffusion) emerging at the moment, and is currently in beta. The user enters text prompts, and the software generates images based on the associations therein.
Understanding Blockchain
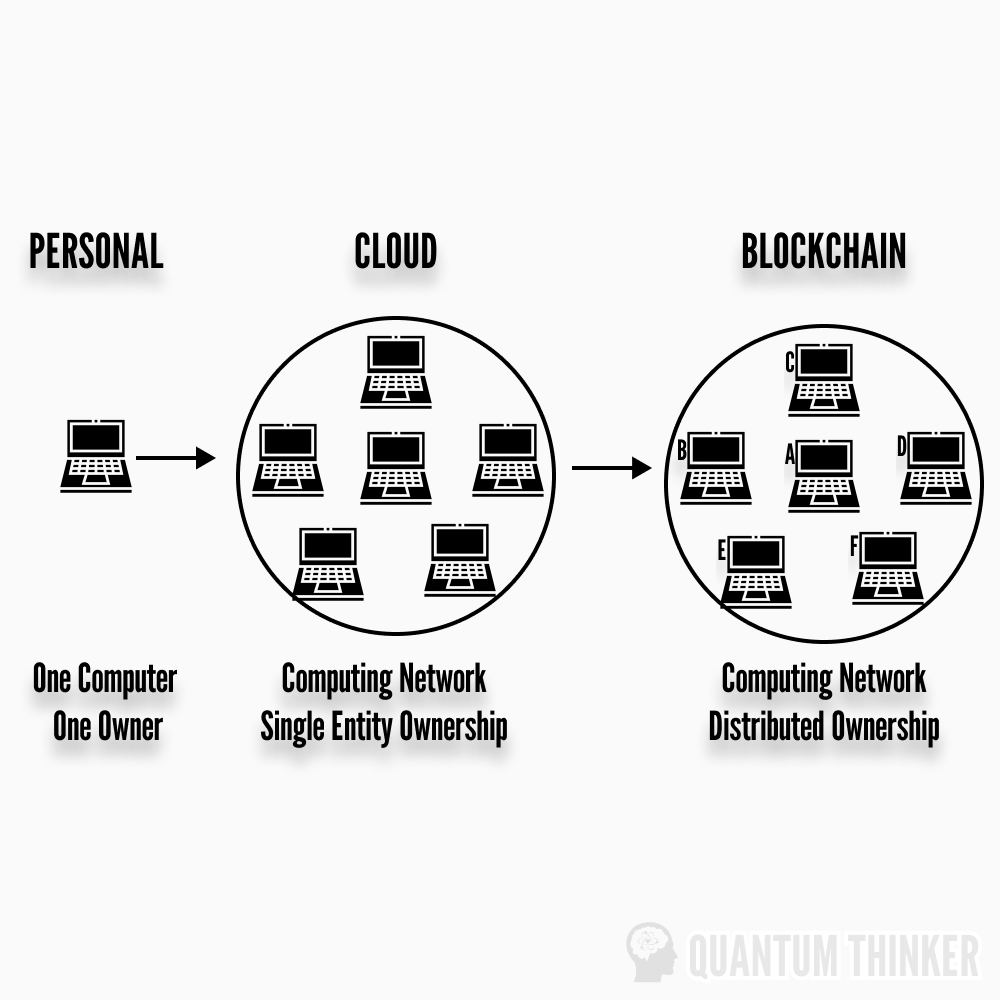
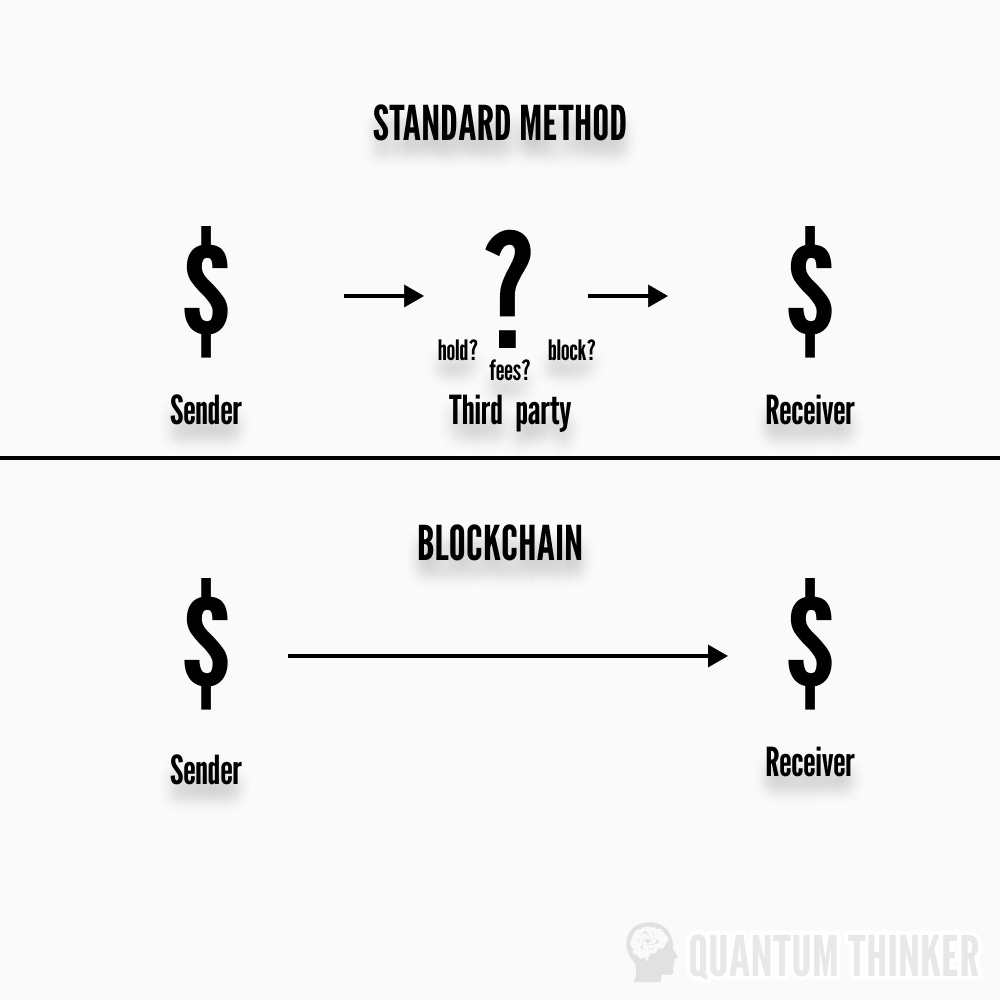
On the other hand, A blockchain refers to a database or distributed ledger technology (DLT) shared between nodes (computers) on a network. They are primarily known for their role when it comes to cryptocurrencies such as Bitcoin and Ethereum, enabling them to maintain a decentralized and secure record of transactions that have taken place on the network. Blockchain also ensures complete transparency, as all recorded transactions can be verified, ensuring that the data can be trusted without the involvement of any third party. Unlike traditional centralized databases, which are managed by a single entity, blockchains are decentralized databases, with the data spread across multiple nodes on the network. Each computer holds an identical copy of the decentralized ledger, meaning any change to the data would require all the data on all nodes to be changed simultaneously. This feature essentially makes the blockchain tamper-proof.
“Society gives you money for giving society what it wants, Blockchains give you coins for giving the network what it wants.” - Naval Ravikant
“The blockchain symbolizes a shift in power from the centers to the edges of the networks.” - William Mougayar
“The Internet is programmable information. The blockchain is programmable scarcity.” - Balaji Srinivasan
Let’s, get into deep dive the key terms of Blockchain
1) Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT)
Fundamentally, it maintains an encrypted, unchangeable record of transactions across a vast network of nodes (i.e. computers). Every node retains a complete history of transactions, improving security and making bad behaviour difficult and expensive. DLT goes further than “cloud” computing because it distributes ownership in addition to computing power and storage. Anybody can operate a node, becoming an integral member of the network. The concept may not seem like much at first, but it underpins the remaining properties.
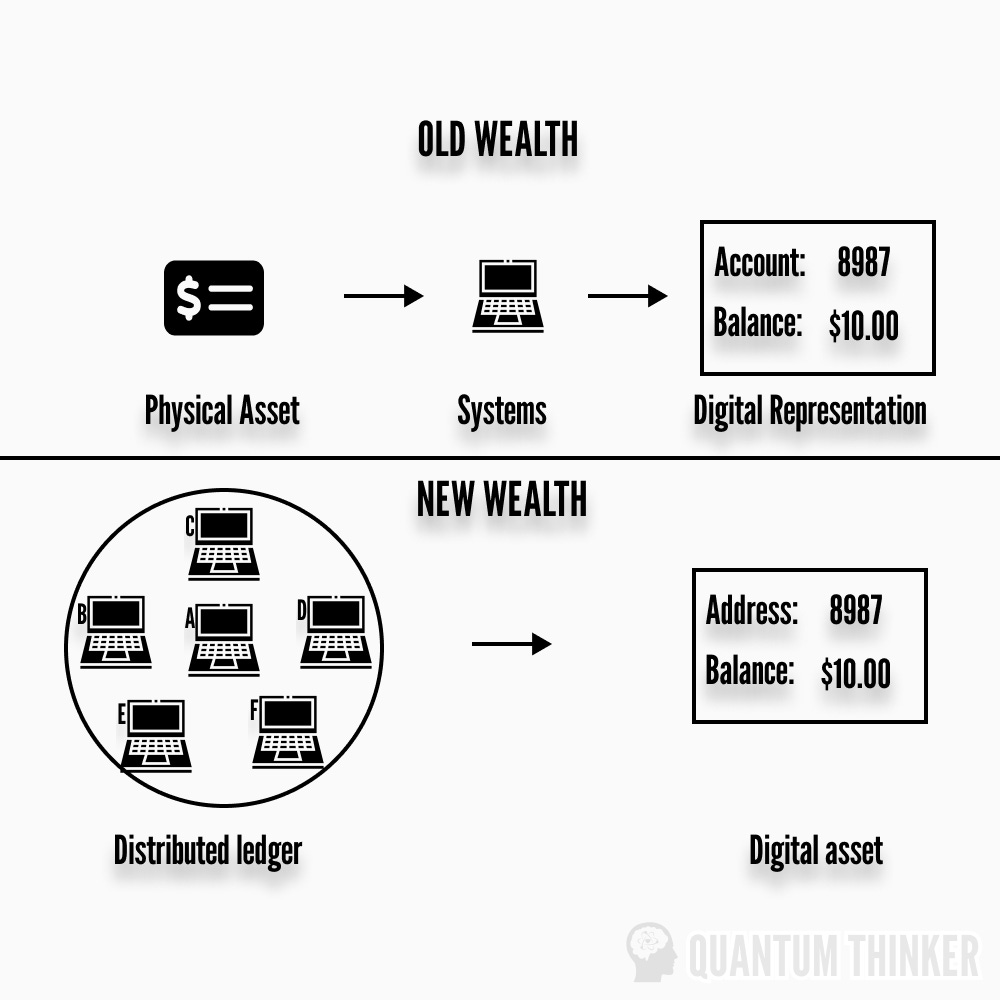
2) Digital Scarcity
Thanks to DLT, we can digitally create and manage currencies without a corresponding physical item. For the first time, we can create digital assets that are reliably limited in quantity.
The applications of this technology extend further than “currencies”. You can create utility tokens (like stocks with a business use-case), digital collectables (NFT), ID anonymity, ticketing systems, distributed cloud networks, financial instruments, etc.
3) Censorship Resistant
Blockchain networks enable peer-to-peer transactions. Third parties are not required to facilitate transactions, unlike bank transfers. You retain full custodianship of your assets whilst being able to pay people directly. Why is this important?
When sending money via third parties (e.g. banks, western union, SWIFT, etc.), it may be blocked, delayed or have hefty fees applied. Intermediaries can occasionally be helpful (e.g. fraud prevention) — but not always.
4) Immutable Smart Contracts
A significant milestone in the life of DLT was the introduction of smart contracts. These are public, immutable blocks of code on the network. Smart contracts give blockchain developers new superpowers. Previously, developers sent information via code. Now, they can send value. Making value transfer programmable opens up a world of opportunities. One area this has immediate implications on is finance.
The code being “on-chain” makes it’s publicly accessible and immutable. Aside from some public parameters, nobody can change the code in the future. The public can audit the code and possesses the agency to enter or leave ecosystems. Open, permanent code will redefine how we view security, transparency, and companies altogether.
“The last era was big data. The next era is verifiable data.” - Balaji Srinivasan
Academics used the earliest versions of the internet to share information. Now, we use it for business, shopping and TikToks. Blockchain technology may appear attractive now, but it presents incredible future opportunities. Smart contracts are the most significant advancements to date. They provide a glimpse into the future—for example, they enable a new level of software autonomy.
5) Autonomous Protocols
Imagine a company automated every single one of its business operations. Eventually, the owner fires everyone because they’re nonessential, and it’s more profitable. Theoretically, if the owner passed away, the business could continue functioning without him for years, without anyone knowing.
If companies operating without human intervention were a norm, how would the world look?
The future is now. For the first time in history, non-human entities can own and transact value. However, smart contracts take this idea a step further. These autonomous protocols are carrying out the functions of a company without any human intervention via the blockchain. Once this tech installed in normal machines such as cars, washing machine, AC, it will be termed as Economy of Things (EOT).
This type of code could completely redefine the concept of a “company”. What do you call ownerless systems that have the power to execute business operations? We’re embarking upon new terrain—automation 2.0. Protocols like Uniswap and Aave function more like money machines than companies because they can thrive without human maintenance.
Autonomy can take other forms too. For example, consider decentralised autonomous organisations (DAO) - algorithmic organisations with encoded governance. Smart contracts can dictate different levels of authority, behaviours and even upgrades. It’s becoming common for community votes to dictate roadmaps, partnerships and to remove bad players.
Combined values of AI and Blockchain
Authenticity
Blockchain's digital record provides visibility into the AI framework and the provenance of the data it uses, answering the difficulty of explainable AI. This increases confidence in the accuracy of the data and, consequently, in the suggestions that AI generates. An audit trail is created when AI models are stored and distributed via blockchain and combining blockchain with AI can improve data security.
Augmentation
AI can instantly and fully scan, analyse, and correlate data, adding a new level of intelligence to blockchain-based business networks. Blockchain enables AI to expand by managing data consumption and model sharing, enabling access to vast amounts of data from both inside and outside the enterprise, and producing a reliable and open data market.
Automation
Combining AI, Blockchain, and automation may provide new value to business operations involving numerous stakeholders by reducing friction, boosting speed, and boosting productivity. For instance, AI models incorporated into smart contracts running on a blockchain can suggest recalled goods that are past their expiration dates, carry out transactions (like stock purchases or reorders based on predetermined thresholds and events), settle disputes, and choose the most environmentally friendly shipping method.
Combined Actual Use Cases
Artificial Intelligence and Blockchain technology are frequently credited with ushering in the fourth industrial revolution, with their implementation revolutionizing industries such as healthcare, finance, supply chain, and logistics.
Healthcare
In the healthcare industry, blockchain and AI have enabled the secure storage of patient data. Healthcare professionals can access this data and study insights from the data thanks to patterns generated by AI that analyses the patient data. Using blockchain and AI, the healthcare industry was able to traverse the minefield that was the Covid-19 outbreak.
Finance
AI and Blockchain have completely transformed the banking sector, enabling trust between parties to interact at much faster and more secure rates. Eliminating third parties in these transactions also ensures that transactions are cheaper. Meanwhile, using AI reduces the dependency on humans, further increasing efficiency.
Supply Chain
In supply chain and logistics industry, where blockchain technology and AI are traditionally transforming the industry by digitizing paper-based processes, making them far more streamlined and effective.
Conclusion
In the future, integrations of AI and blockchain could revolutionize a variety of sectors. They could have wide-ranging applications in finance, smart cities, autonomous vehicles, manufacturing, agriculture, etc.
We’ve already seen some impressive start-ups leveraging OpenAI’s GPT-3. Now, GitHub joined the club with its newly launched product, Co-pilot. It automatically writes your code. No joke. The system has been “trained on billions of lines of public code”, and its capabilities are scary.
“Artificial intelligence would be the ultimate version of Google. The ultimate search engine that would understand everything on the web. It would understand exactly what you wanted, and it would give you the right thing. We’re nowhere near doing that now. However, we can get incrementally closer to that, and that is basically what we work on.” - Larry Page
Crypto is redefining life as we know it. The idea of autonomous smart contracts, community-owned networks and DAOs may eventually become the new normal. It’s even challenging the need for privately-owned companies. Providing ownership through governance directly to the end-users may create more alignment, and better incentives could accelerate progress.
"Learning and innovation go hand in hand. The arrogance of success is to think that what you did yesterday will be sufficient for tomorrow.” — William Pollard
Thanks for reading...
Follow for visuals at | Facebook | Twitter | Instagram | LinkedIn | Pinterest | Reddit |